Ceribell White Paper:
The Impact of Ceribell at the Bedside
How does point-of-care EEG influence the management of patients?
To measure the real-world impact of bedside point-of-care EEG, Ceribell conducted a nationwide, in-device survey to capture how clinicians use POC EEG results to inform clinical decisions, patient management strategies, and hospital resource allocation.
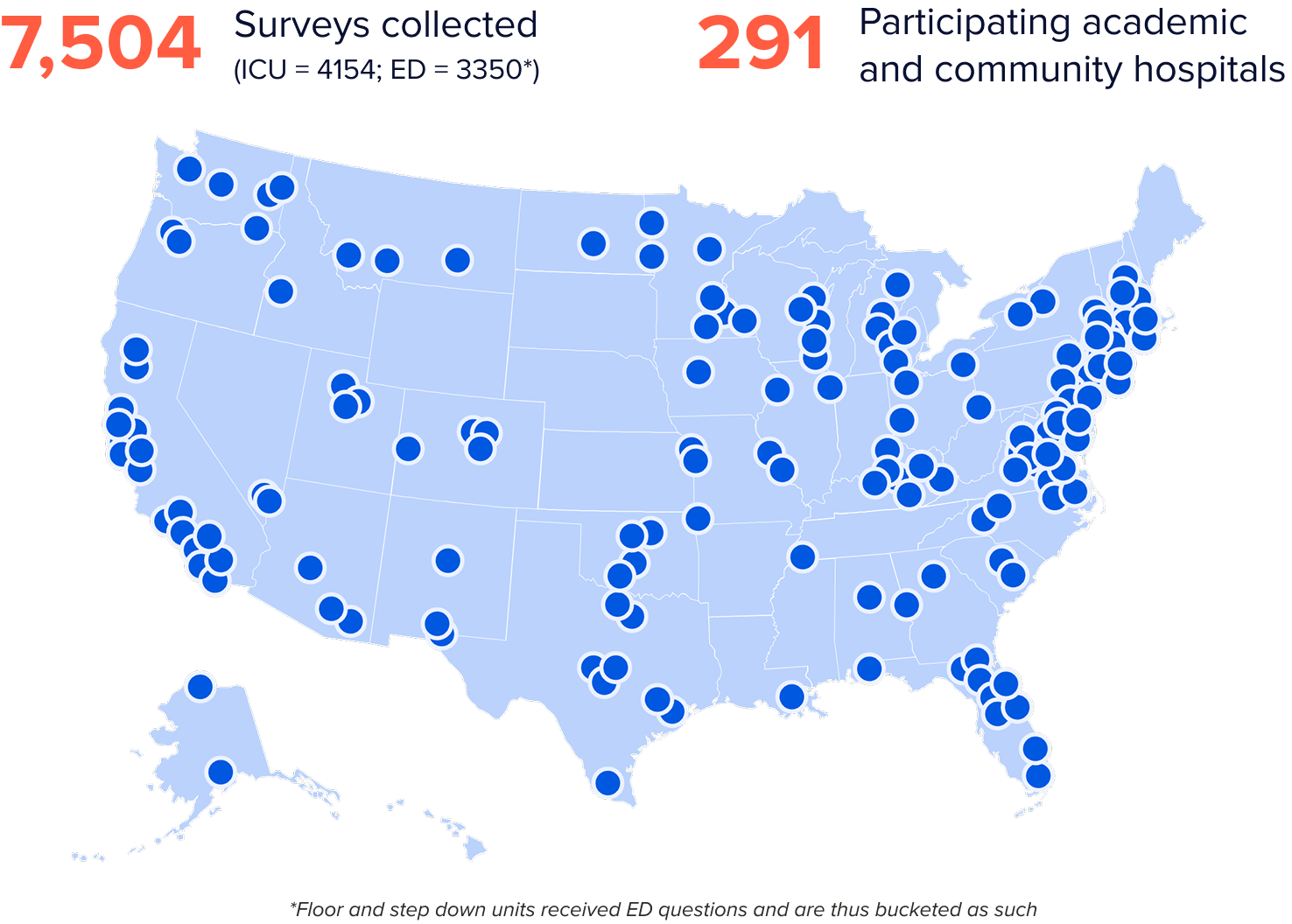
Key Survey Findings
By providing realtime, actionable insights, Ceribell:

Improved decision making

Reduced unnecessary ASMs and intubations

Prevented avoidable ICU admissions and transfers
Read the full whitepaper to explore how emergency departments (ED) and intensive care units (ICU) are using point-of-care seizure data to improve clinical decision making, and achieving operational benefits, such as avoiding unnecessary medication, intubation, ICU admission and hospital transfers.
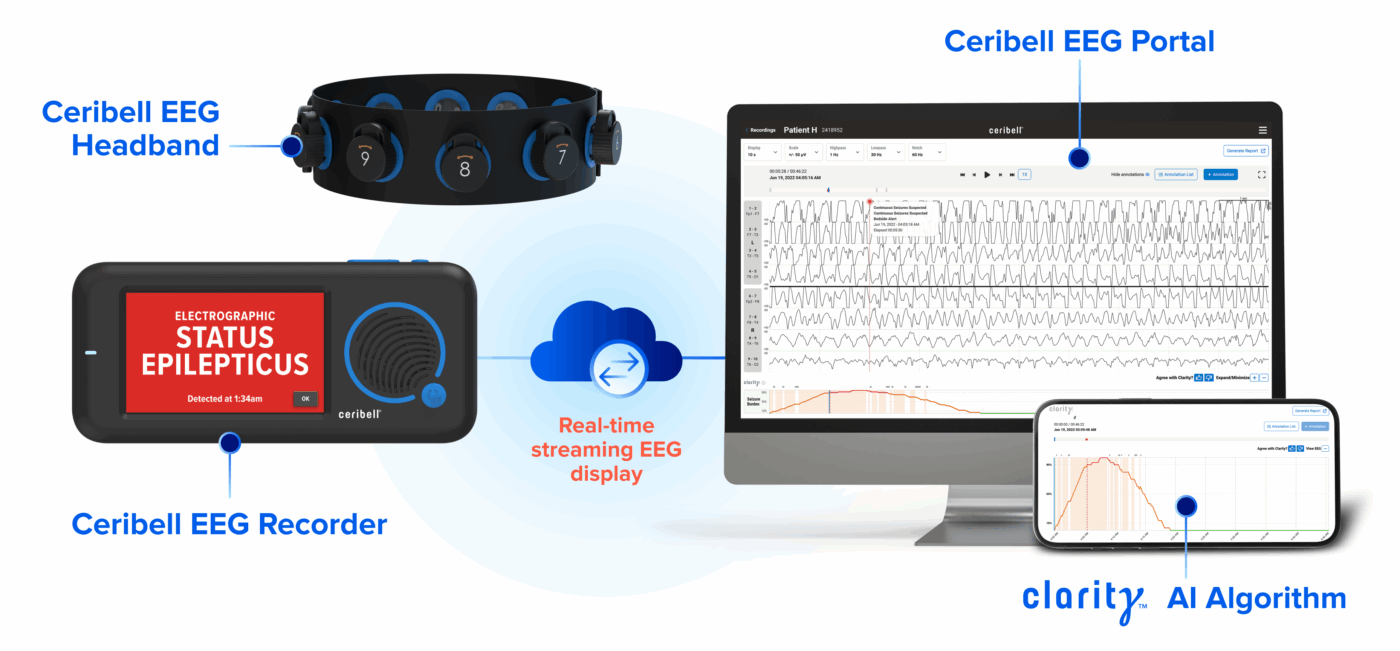
What is point-of-care EEG?
Non-convulsive seizures are common in critically ill ED and ICU patients.1,2 These seizures are serious3 but difficult to diagnose without EEG4,5. Point-of-care EEG helps enable access to critical EEG data in acute care settings. The Ceribell EEG System includes a disposable headband and pocket-sized recorder, allowing healthcare professionals to begin EEG monitoring in minutes with minimal training. Real-time streaming of EEG data to a cloud-based portal enables physicians to review EEG data with pre-annotated insights.

Resources
Fox Business News: Doctors using AI-driven devices to help detect seizure activity in patients
Read MoreIn The News
Ceribell Announces Publication of Study Demonstrating Significant Reduction in Length of ICU Stays and Better Patient Outcomes with Ceribell Point-of-Care EEG Compared to Conventional EEG
Read MorePress Release
Leading healthcare providers and EEG experts discuss the latest clinical evidence highlighting how Ceribell Point-of-Care EEG is impacting patient care for at-risk patients.
Learn MoreEEG UNIVERSITY
References and Citations
1. Herman, S.T., et al. (2015) J Clin Neurophysiol. 32(2):87-95
2. Zehtabchi, S., et al. (2013). Am J Emerg Med, 31(11), 1578-82
3. Trinka, E., et al. (2015) Epilepsia. 56(10):1515-1523
4. Claassen, J., et al. (2004). Neurology. 62(10):1743–1748
5. Rudin, D., et al. (2011) Epilepsy Res. 96(1-2):140-50