The FIRST critical care monitoring device and neurodiagnostic device to achieve both





Revolutionizing Neurodiagnostics with AI

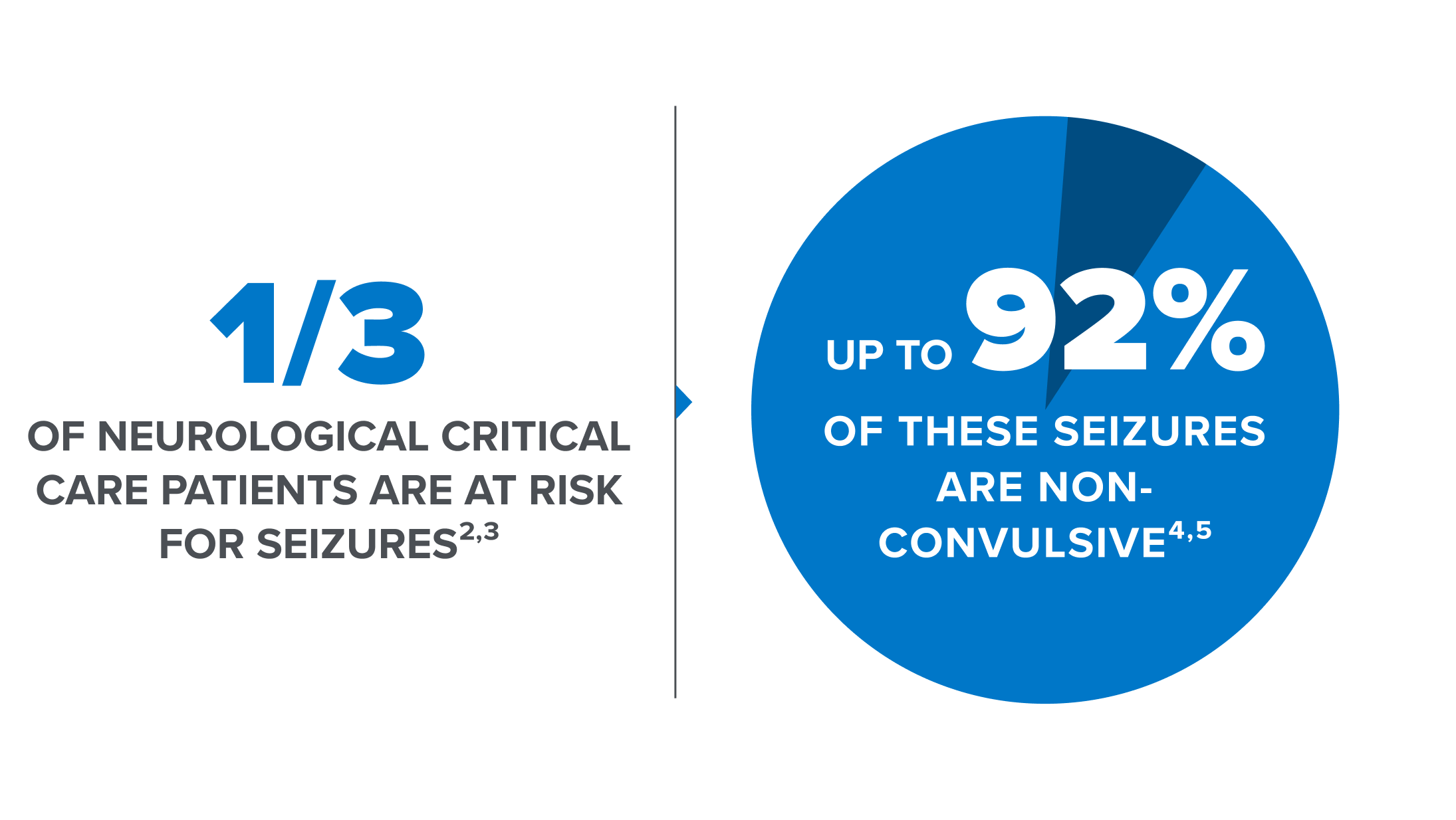
Non-convulsive seizures are prevalent in critically ill patients1
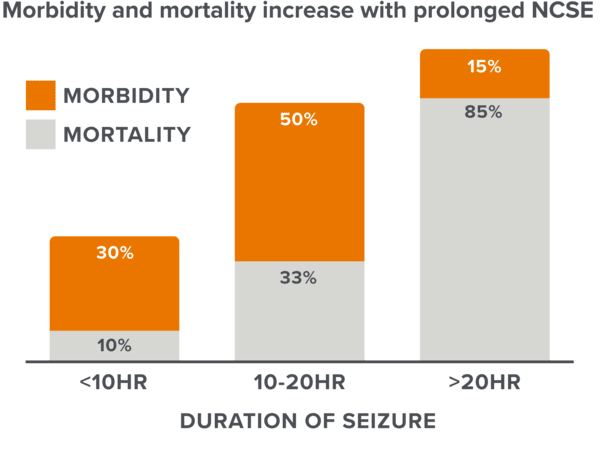
Time to treatment is critical6
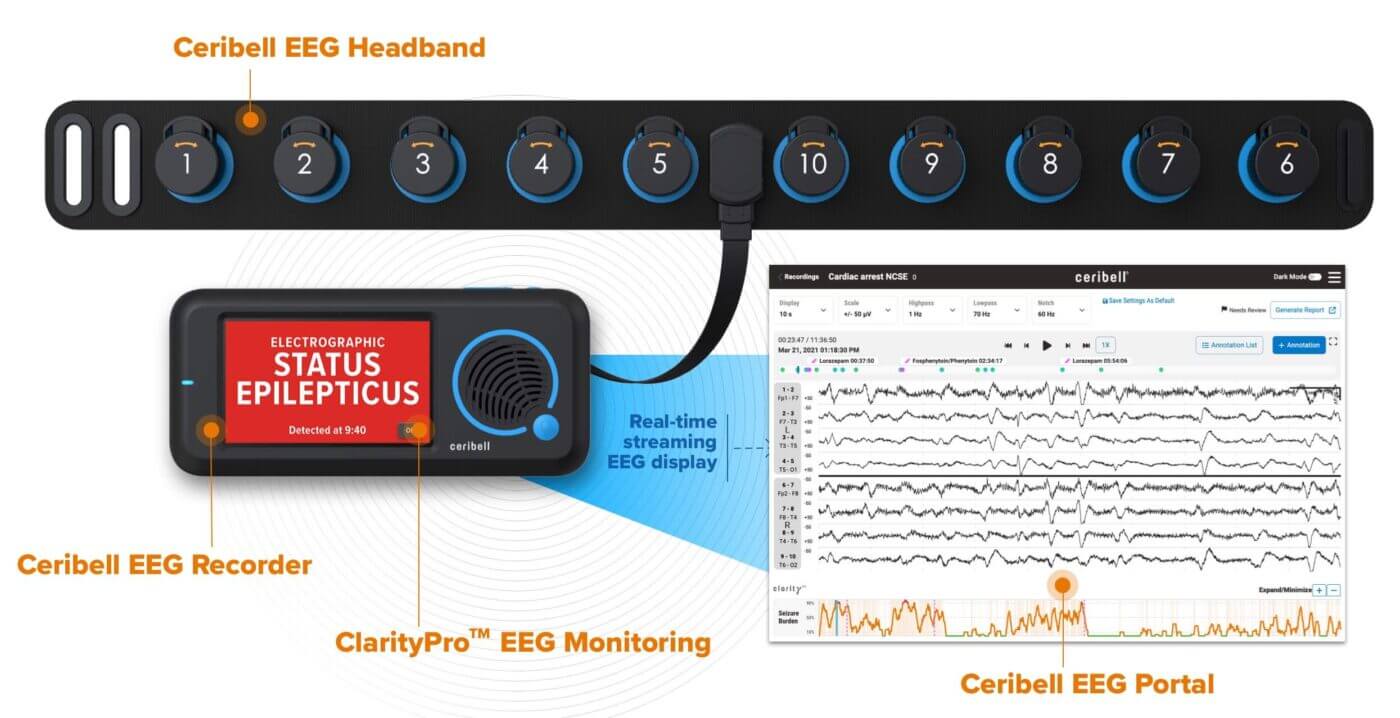
Ceribell Point-of-Care EEG


Resources
Fox Business News: Doctors using AI-driven devices to help detect seizure activity in patients
Read MoreIn The News
Press Release
Leading healthcare providers and EEG experts discuss the latest clinical evidence highlighting how Ceribell Point-of-Care EEG is impacting patient care for at-risk patients.
Read MoreEEG UNIVERSITY
References and Citations
1. Herman, S.T., et al. (2015) J Clin Neurophysiol. 32(2):87-95
2. Laccheo, I., et al. (2015) Neurocrit Care. 22:202-211
3. De Marchis, G.M., et al. (2016) Neurology. 86(3):253-260
4. Claassen, J., et al. (2004). Neurology. 62(10):1743-1748
5. Rudin, D., et al. (2011) Epilepsy Res. 96(1-2):140-150
6. Young, G.B., et al. (1996). Neurology, 47(1):83-89